 欢迎来到方临川研究员“土壤生态与环境课题组”
欢迎来到方临川研究员“土壤生态与环境课题组”

 欢迎来到方临川研究员“土壤生态与环境课题组”
欢迎来到方临川研究员“土壤生态与环境课题组”

您的位置:科研进展 >科研动态>专题总结
土壤微生物组与土壤健康关系密切,深入揭示微生物之间相互作用的机制和微生物组的整体功能,加强对土壤微生物组组成及功能的研究,利用微生物修复污染土壤以提升土壤健康,对维持农业可持续生产和保护环境至关重要。近三年来,水保所土壤生态与环境课题组在土壤-植物-微生物互作过程及其重金属污染土壤的植物-微生物修复技术等方面取得了系列进展:
1. 微生物-土壤-植物互作方面:建立了污染土壤中根-土界面酶活性的原位测定方法,阐明了根系分泌物与微生物群落间的密切相关性,揭示了微生物-根系的相互作用机制。根-土界面上酶活性及空间分布的原位表征一直是土壤学领域研究的热点和难点。我们建立了重金属污染土壤中根-土界面酶活性的原位测定方法,获得了土壤关键酶活性在根-土界面上的二维空间分布特征(图 1; Duan et al., 2018, 2019),这将土壤酶学的研究从以往传统破坏性采样转变到原位定量获取二维直观信息。此外,我们发现植物丰富度影响根系分泌物的组成,105种根系分泌物组分(糖类、胺、羧酸、酚类以及脂类)中,糖类和脂类含量随植物丰富度的增加而升高。根系分泌物多样性与微生物群落多样性和均匀度呈显著正相关;植物通过改变根系分泌物的多样性来影响微生物多样性(图 2; Zhang et al., 2019)。
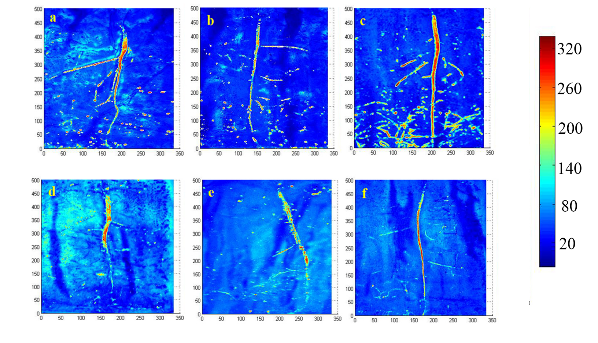
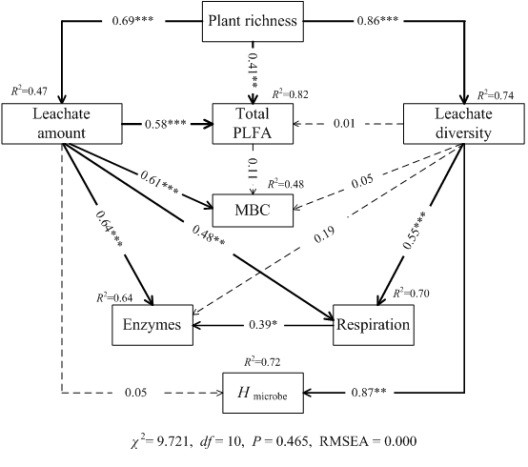
图 1. 不同污染程度下根际酶活性二维空间分布 图 2. 根系分泌物对微生物多样性影响的SEM分析
2. 重金属污染土壤中功能菌筛选及基因工程菌构建方面:从陕西省凤县铅锌矿区污染农地中分离出一株铅抗性菌株粘质沙雷氏菌Serratia Se1998,抗铅浓度可达40 mM,添加到黑麦草和小麦盆栽体系中能显著促进植物生长,提高植物抗铅胁迫。且该菌株对铅具有较强的固定能力,既可依靠细胞壁表明官能团(羧基、磷酸基团)吸附Pb,又可以依靠鞭毛蛋白结合Pb,从而降低Pb的生物有效性(图3; Chen et al., 2019a)。Serratia Se1998接种到黑麦草和小麦根际均能显著降低铅在植物组织中的积累。同时,我们人工合成了Serratia Se1998的铅结合蛋白Flagellin,并通过重组质粒将Flagellin基因转入大肠杆菌,深入分析了该基因在铅胁迫下的作用与功能,发现转MFlagellin基因的大肠杆菌在蛋白表达量和铅的吸收率上有明显地提高。在此基础上,我们结合宏观及微观技术手段,从分子层面揭示了Pb(II)在Serratia Se1998、Serratia Se1998-水铁矿复合体表面吸附的微观结构(图4; Chen et al., 2019b, 2020)。上述结果表明Serratia Se1998对于铅在根-土界面的形态调控、降低其生物可给性及在土壤-植物系统中的迁移能力有重要潜力。
超积累植物,是指能超量吸收重金属并将其运移到地上部积累的植物。目前已经被发现的有400多种超积累植物。紫花苜蓿属于豆科为多年生草本,根系粗壮,根茎发达,为直根系植物。紫花苜蓿是我国主要的常见牧草之一,在我国各地均有分布,且其具有丰富的蛋白质、膳食纤维、矿物质和维生素等营养成分等。豆科植物根瘤菌共生在生态和农业上起着重要的作用,以前的研究表明根瘤菌促进植物生长,增强植物抵御环境压力的能力。例如,豆科植物主要在根部积累重金属,并表现出较低水平的金属迁移到地上部(Pajuelo et al., 2008, Pajuelo et al., 2011)。
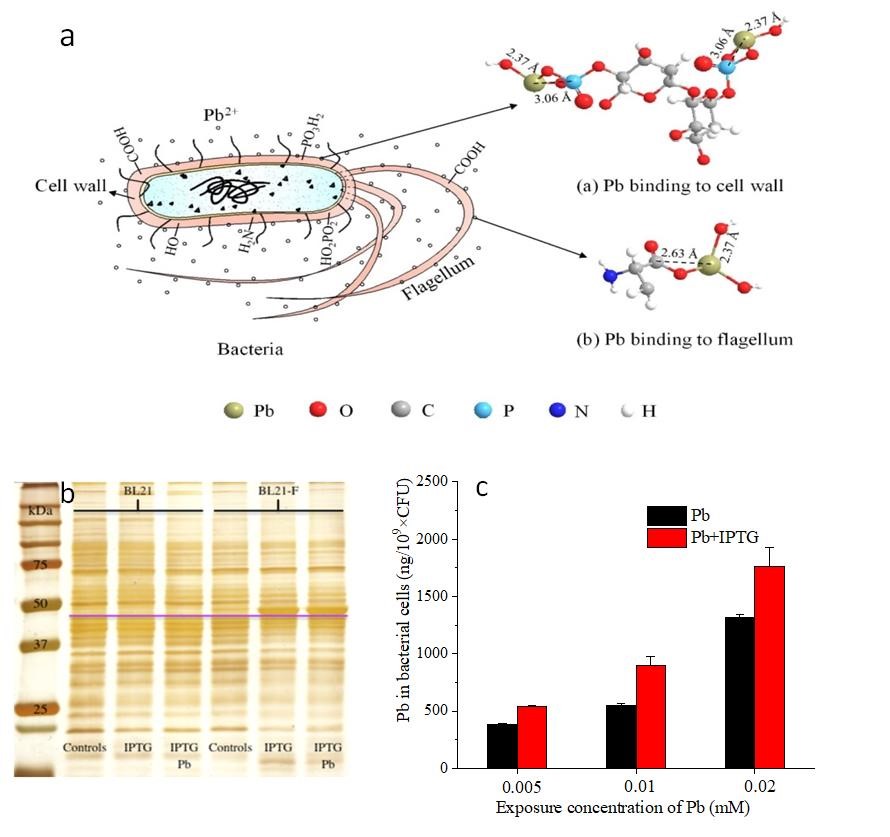
图 3. (a)Serratia Se细胞壁和鞭毛蛋白吸附Pb,(b)鞭毛蛋白在大肠杆菌中的表达,(c)重组后表达鞭毛蛋白的菌株对Pb的吸收
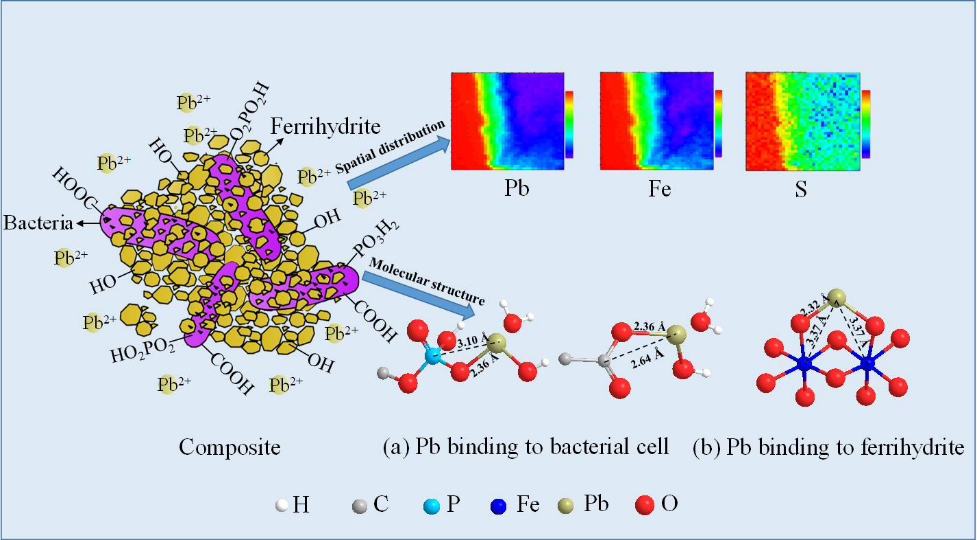
图 4. Pb(II)在水铁矿-细菌复合体表面结合的空间分布和分子结构
3. 重金属污染土壤体系中的多功能微生物组阻控体系构建方面:从重金属污染土壤中筛选了多株功能菌,通过优化、组配,构建的功能菌组阻控体系提高了植物抗性,降低了重金属在植物地上部分的积累。基于西北矿区土壤贫瘠、气候干燥、风力大、雨量少且集中、易水土流失的客观基础,结合西北地区作物种植模式,我们构建的根瘤菌-苜蓿共生体系(Chen et al., 2018)、根瘤菌-芽孢杆菌-苜蓿体系(图5; Ju et al., 2018; Ju et al., 2020a)显著提升了土壤氮素供应能力,增加了植物生长促生菌( Nocardioides,Rhizobium,Glycomyces)丰度,提高了植物重金属抗性,降低铅、镉在土壤-植物系统中迁移风险;我们构建的根瘤菌-丛枝菌根真菌-苜蓿体系(Wang et al., 2021)发现Proteobacteria,Actinobacteria,Acidobacteria和Chloroflexi作为关键细菌类群在促进苜蓿根际养分吸收和提高Cd抗性中扮演了重要的角色(图6; 图 7);对矿区周边不同土地利用类型(农地、草地、林地)下重金属的形态毒性分析,并结合环境风险评价模型预测,提出林地是矿区周边污染土地的较安全利用方式(Fang et al., 2017a; Tian et al., 2018)。
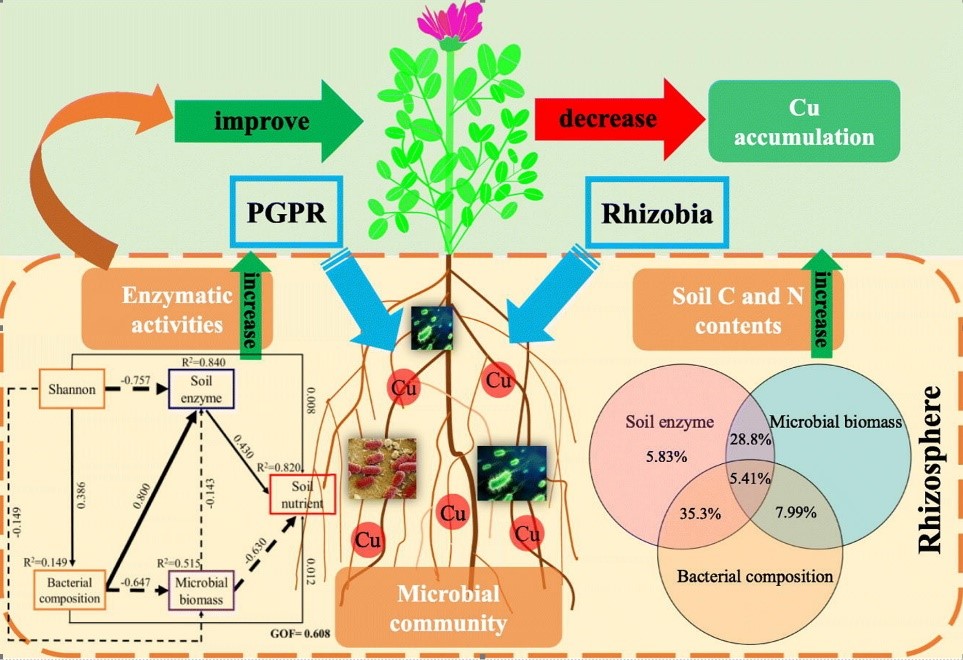
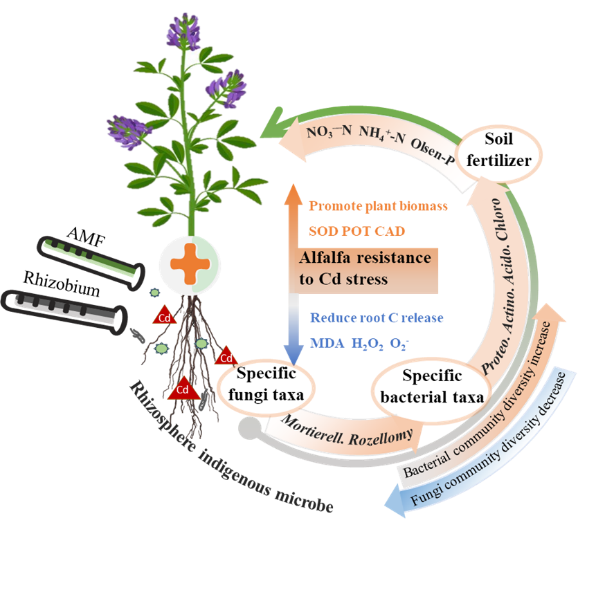
图 5. 双接菌(根际促生菌-根瘤菌)提高苜蓿Cu抗性和降低Cu吸收 6: 双接菌(丛枝菌根真菌-根瘤菌)提高苜蓿Cd抗性和降低Cd吸收
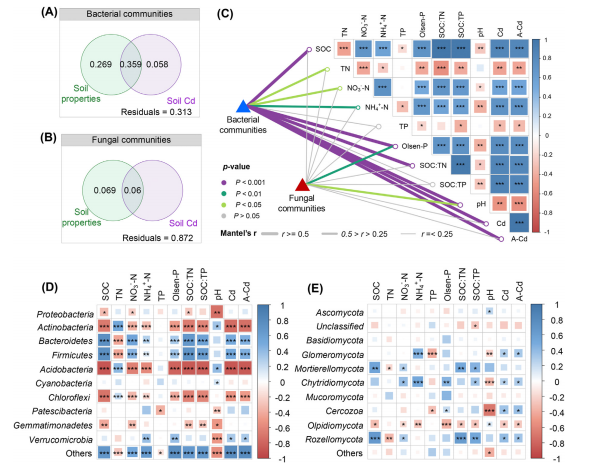
图 7. 双接菌(丛枝菌根真菌-根瘤菌)对Cd污染土壤理化性质和微生物群落的影响
4. 提高植物抗重金属胁迫方面:重金属污染土壤上生长的植物会受到严重抑制。已有研究表明氮肥的施用及信号分子(H2S和NO)在提高植物逆境胁迫方面有较好作用,但在重金属污染土壤植物修复方面的应用及相关机制仍不清楚。我们研究发现H2S和NO加入通过增加抗氧化酶活性和抑制豆科植物-根瘤菌共生体系中的脂质过氧化和活性氧水平来减轻金属诱导的植物毒性(图8; Fang et al., 2019)。此外,信号分子改善了土壤养分循环,提高了土壤酶活性,促进了根际细菌群落多样性;N素在提高植物重金属提取效率和抑制植物抗氧化损伤方面有显著作用(Shen et al., 2019; Fang et al., 2020);螯合诱导修复体系中EDDS释放的N能提高植物生物量,增强植物抗重金属胁迫能力(图9; Fang et al., 2017b; Ju et al., 2020b; Beiyuan et al., 2021)。
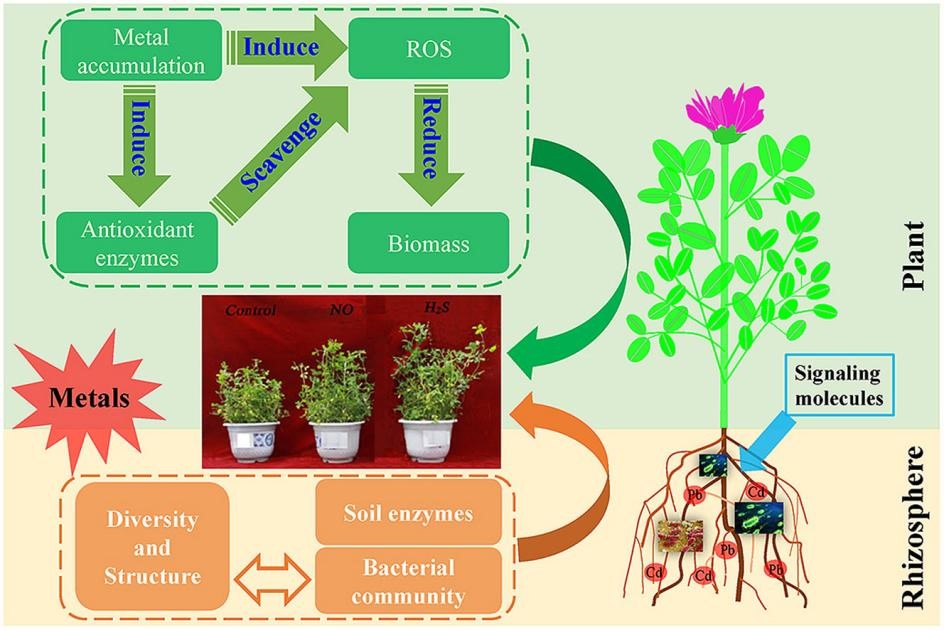
图 8. 信号分子添加在提高植物逆境胁迫方面的示意图
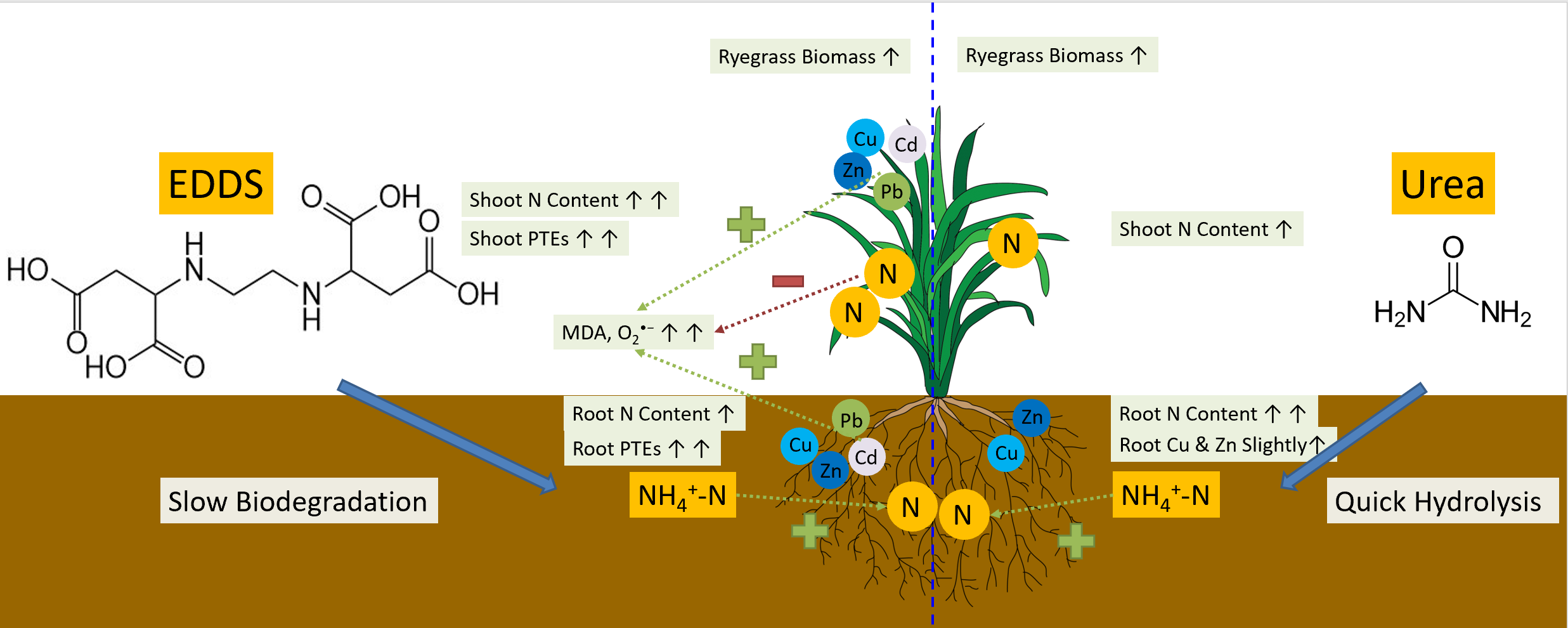
图 9. 螯合诱导修复体系中N素增强植物抗重金属胁迫的示意图
1. Chengjiao Duan, Linchuan Fang*, Congli Yang, Weibin Chen, Yongxing Cui, Shiqing Li. Reveal the response of enzyme activities to heavy metals through in situ zymography. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety. 2018, 156, 106-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.015 (ESI前1%高被引论文)
2. Chengjiao Duan, Bahar S. Razavi, Guoting Shen, Yongxing Cui, Wenliang Ju, Shiqing Li, Linchuan Fang*. Deciphering the rhizobium inoculation effect on spatial distribution of phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere of alfalfa under copper stress. Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 2019, 137, 107574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107574
3. Chao Zhang, Jie Wang, Guobin Liu, Zilin Song, Linchuan Fang*. Impact of soil leachate on microbial biomass and diversity affected by plant diversity. Plant and Soil. 2019, 505-523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04032-x
4. Guoting Shen, Wenliang Ju, Yuqing Liu, Xiaobin Guo, Wei Zhao, Linchuan Fang*. Impact of urea addition and rhizobium inoculation on plant resistance in metal contaminated soil. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019, 6, 2-17. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/ijerph16111955
5. Baowei Chen#, Linchuan Fang#, Xueting Yan, Aiqian Zhang, Ping Chen, Tiangang Luan, Ligang Hu*, Guibin Jiang. A unique Pb-binding flagellin as an effective remediation tool for Pb contamination in aquatic environment. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2019a, 363, 34-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.004
6. Hansong Chen, Jinling Xu, Wenfeng Tan, Linchuan Fang*. Lead binding to wild metal-resistant bacteria analyzed by ITC and XAFS spectroscopy. Environmental Pollution. 2019b, 250, 118-126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.123
7. Hansong Chen, Wenfeng Tan, Wei Lv, Juan Xiong, Xiaoming Wang, Hui Yin, Linchuan Fang*. Molecular Mechanisms of Lead Binding to Ferrihydrite−Bacteria Composites: ITC, XAFS, and μ‑XRF Investigations. Environmental Science and Technology. 2020, 54, 4016-4025. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06288
8. Tuantuan Cui, Linchuan Fang*, Mengke Wang, Mao Jiang, Guoting Shen. Intercropping of gramineous pasture ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and leguminous forage alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) increases the resistance of plants to heavy metals. Journal of Chemistry. 2018, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7803408
9. Haixia Tian, Linchuan Fang*, Chengjiao Duan, Yunqiang Wang, Hao Wu. Dominant factor affecting Pb speciation and the leaching risk among land-use types around Pb-Zn mine. Geoderma. 2018, 326, 123-132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.04.016
10. Jingzi Beiyuan, Linchuan Fang*, Hansong Chen, Mengdi Li, Dongdong Liu, Yunqiang Wang. Nitrogen of EDDS enhanced removal of potentially toxic elements and attenuated their oxidative stress in a phytoextraction process. Environmental Pollution. 2021, 268, 115719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115719
11. Juan Chen, Yuqing Liu, Xiaowu Yan, Gehong Wei, Jianhua Zhang, Linchuan Fang*. Rhizobium inoculation enhances copper tolerance by affecting copper uptake and regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and phytochelatin biosynthesis-related gene expression in Medicago sativa seedlings. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2018, 162, 312-323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.001
12. Linchuan Fang, Yuqing Liu, Haixia Tian, Hansong Chen, Yunqiang Wang, Min Huang*. Proper land use for heavy metal-polluted soil based on enzyme activity analysis around a Pb-Zn mine in Feng County, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2017a, 24, 28152-28164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0308-4
13. Linchuan Fang, Mengke Wang, Lin Cai, Long Cang*. Deciphering biodegradable chelant-enhanced phytoremediation through microbes and nitrogen transformation in contaminated soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2017b, 24, 14627–14636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9029-y
14. Linchuan Fang, Wenliang Ju, Congli Yang, Chengjiao Duan, Yongxing, Fu Han, Guoting Shen, Chao Zhang*. Application of signaling molecules in reducing metal accumulation in alfalfa and alleviating metal-induced phytotoxicity in Pb/Cd contaminated soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2019, 182, 109459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109459
15. Linchuan Fang, Wenliang Ju, Congli Yang, Xiaolian Jin, Dongdong Liu, Mengdi Li, Jialuo Yu, Wei Zhao, Chao Zhang*. Exogenous application of signaling molecules to enhance the resistance of legume-rhizobium symbiosis in Pb/Cd-contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution. 2020, 265, 114744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114744
16. Wenliang Ju, Lei Liu, Linchuan Fang*, Yongxing Cui, Chengjiao Duan, Hao Wu. Impact of co-inoculation with plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobium on the biochemical responses of alfalfa-soil system in copper contaminated soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2018, 167, 218-226. (ESI前1%高被引论文)
17. Wenliang Ju, Xiaolian Jin, Lei Liu, Guoting Shen, Wei Zhao, Chengjiao Duan, Linchuan Fang*. Rhizobacteria inoculation benefits nutrient availability for phytostabilization in copper contaminated soil: Drivers from bacterial community structures in rhizosphere. Applied Soil Ecology. 2020a, 150, 103450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.103450
18. Wenliang Ju, Lei Liu, Xiaolian Jin, Chengjiao Duan, Yongxing Cui, Jie Wang, Dengke Ma, Wei Zhao, Yunqiang Wang, Linchuan Fang*. Co-inoculation effect of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobium on EDDS assisted phytoremediation of Cu contaminated soils. Chemosphere. 2020b, 254, 126724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126724
19. Xia Wang, Linchuan Fang*, Jingzi Beiyuan, Yongxing Cui, Qi Peng, Shilei Zhu, Man Wang. Xingchang Zhang. Improvement of alfalfa resistance against Cd stress through rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi co-inoculation in Cd-contaminated soil. Environmental Pollution. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116758
联系地址:湖北省武汉市武汉理工大学
电 话:15249204460
晋ICP备2020011185号-1
.png)